Conquering Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Clear Skin
Acne affects millions, leaving many frustrated and searching for solutions. This detailed guide breaks down acne treatment options, from basic skincare to advanced medical interventions, helping you navigate the path to clearer skin.
Understanding Your Acne: The First Step
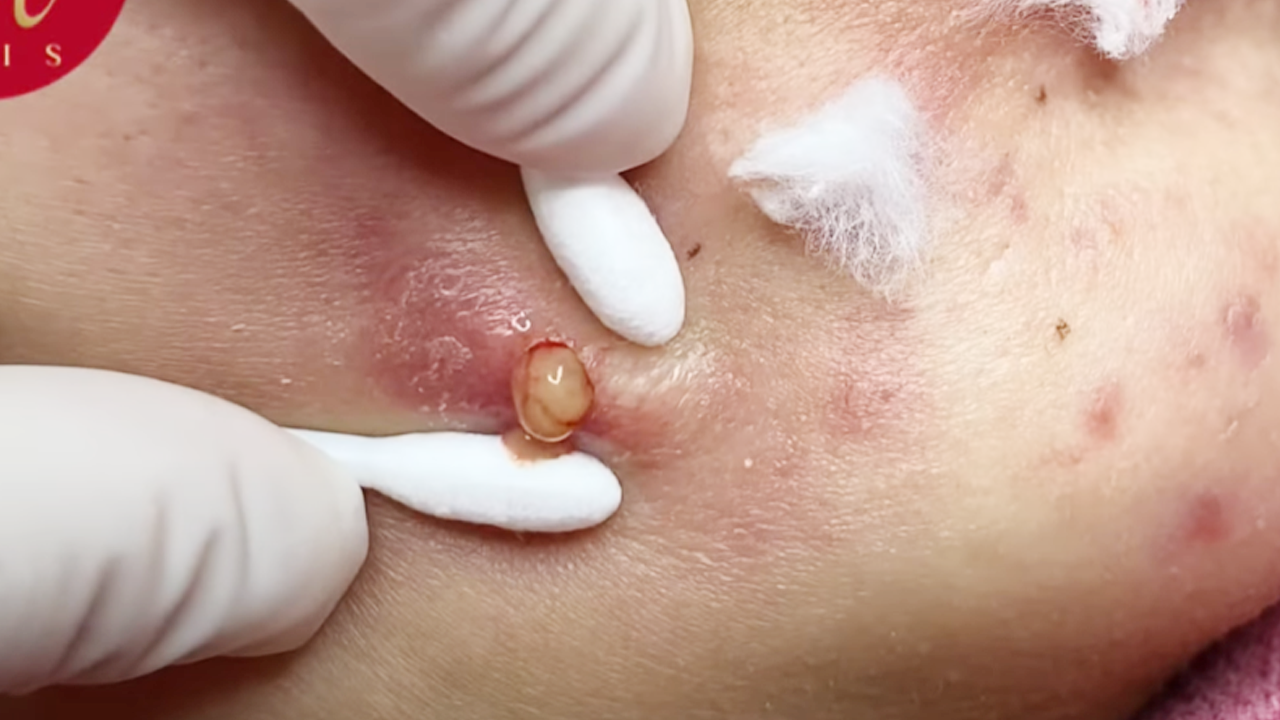
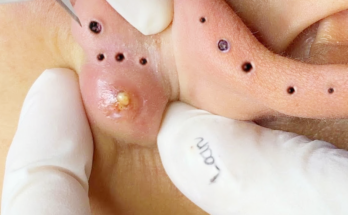
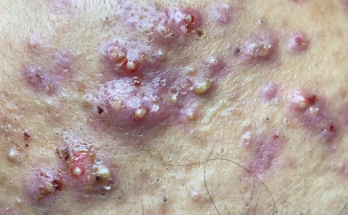
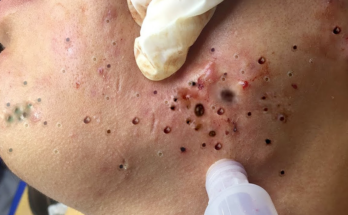
Before diving into treatments, understanding the type of acne you have is crucial. Acne vulgaris, the most common type, arises from clogged pores due to a combination of excess sebum (oil), dead skin cells, and bacteria ( Propionibacterium acnes). Different presentations exist:
Types of Acne:
- Comedonal Acne: This milder form involves blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones), characterized by clogged pores without significant inflammation.
- Inflammatory Acne: This progresses beyond clogged pores, showcasing inflamed papules (small red bumps), pustules (pus-filled bumps), nodules (larger, deeper bumps), and potentially painful cysts.
- Hormonal Acne: Often linked to fluctuations in hormone levels, this type frequently appears during menstruation or pregnancy.
Tackling Acne: A Multi-Pronged Approach
Effective acne management often requires a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs and acne severity.
Basic Skincare: The Foundation
Even with mild acne, a consistent skincare routine forms the bedrock of treatment:
- Gentle Cleanser: Twice-daily cleansing with a non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) cleanser removes excess oil and debris.
- Oil-Free Moisturizer: Even oily skin needs hydration; choose a non-comedogenic, oil-free moisturizer to maintain skin’s barrier function.
- Daily Sunscreen: Sun protection is vital, even with acne. Opt for a broad-spectrum, non-comedogenic sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments: Initial Intervention
Several effective OTC treatments can address mild to moderate acne:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This powerful antibacterial agent kills P. acnes and reduces inflammation. Available in various concentrations (2.5%, 5%, 10%), start with a lower concentration to minimize irritation.
- Salicylic Acid: This beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) exfoliates the skin, unclogging pores and preventing future breakouts.
- Adapalene (Differin): A retinoid derivative, adapalene promotes cell turnover, reducing clogged pores and inflammation. Remember to apply it at night.
Prescription Treatments: Targeting Moderate to Severe Acne
For moderate to severe acne, a dermatologist can prescribe stronger treatments:
- Topical Retinoids (e.g., Tretinoin): These potent vitamin A derivatives are highly effective but can cause initial irritation.
- Topical Antibiotics (e.g., Clindamycin, Erythromycin): Often used in combination with benzoyl peroxide to combat bacterial resistance.
- Oral Antibiotics (e.g., Doxycycline, Minocycline): These are usually short-term treatments to manage inflammation, often combined with topical therapies.
- Hormonal Therapies (e.g., Birth Control Pills, Spironolactone): For females, hormonal imbalances can contribute to acne. These treatments can help regulate hormones.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): Reserved for severe, cystic acne unresponsive to other treatments, isotretinoin is a powerful medication requiring close medical supervision due to potential side effects.
Lifestyle and Preventive Measures: Supporting Clear Skin
Beyond topical and oral treatments, lifestyle choices play a significant role:
- Avoid Picking or Squeezing: Resist the urge; this can lead to scarring and inflammation.
- Clean Linens: Regularly wash pillowcases and towels to minimize bacterial transfer.
- Hands Off Your Face: Avoid touching your face unnecessarily.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Use makeup and skincare products specifically formulated to avoid clogging pores.
Professional Treatments: Advanced Options
For persistent or severe acne, consider professional treatments:
- Light and Laser Therapies: These can target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Chemical Peels: Exfoliating peels (salicylic, glycolic acid) remove dead skin cells, improving texture and reducing breakouts.
- Steroid Injections: Used for large, inflamed cysts to quickly reduce inflammation and pain.
The Bottom Line: Seeking Professional Guidance
Effective acne treatment is personalized. Consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan based on your specific acne type and severity. Remember, consistency and patience are key to achieving clearer, healthier skin.