Understanding and Treating Sebaceous Cysts: A Comprehensive Guide
Sebaceous cysts, also known as epidermoid cysts, are a common skin condition. This detailed guide will explore what they are, how to manage them, and when professional medical attention is necessary.
What are Sebaceous Cysts?
The Basics
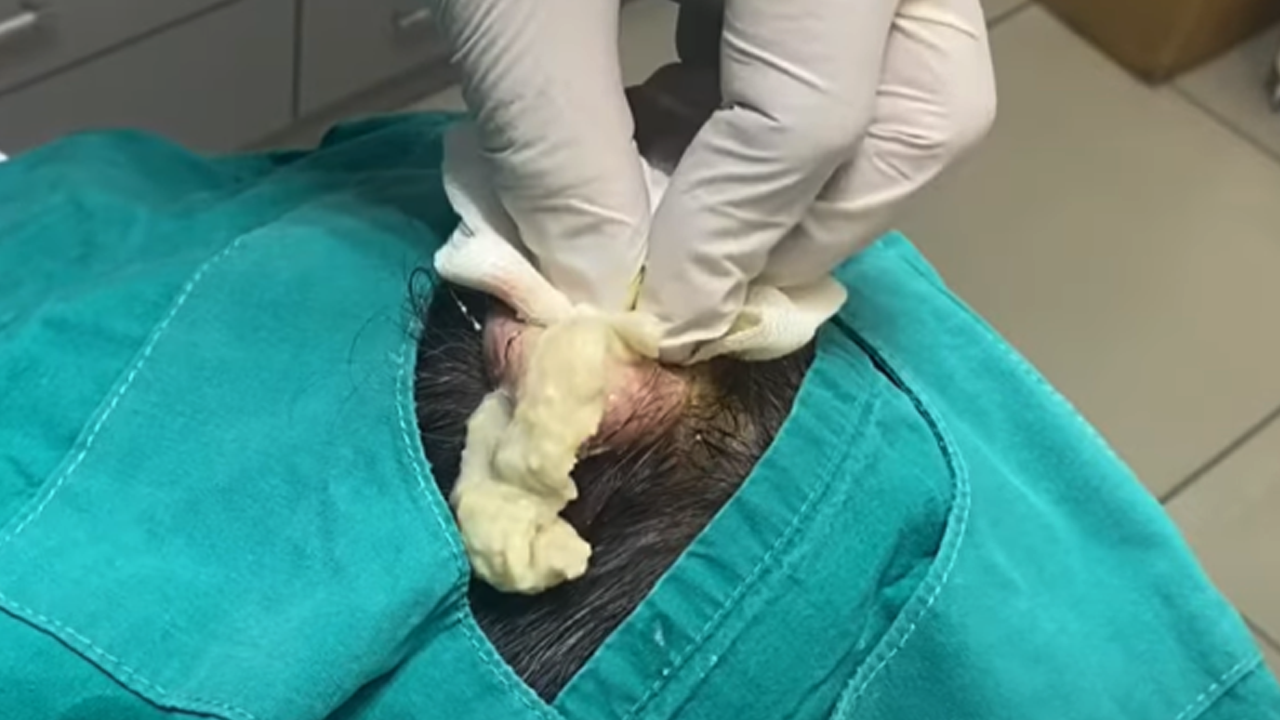
A sebaceous cyst is a benign, slow-growing lump that develops beneath the skin’s surface. It arises from a blocked sebaceous gland—a gland responsible for producing sebum, the oily substance that lubricates our skin. This blockage, often caused by a clogged hair follicle or pore filled with keratin (a skin protein), leads to the accumulation of sebum, forming the characteristic cyst. While painless in many cases, these cysts can appear anywhere on the body, frequently showing up on the scalp, face, back, neck, ears, and trunk.
Appearance and Symptoms
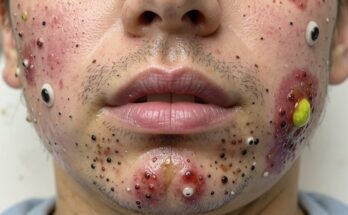
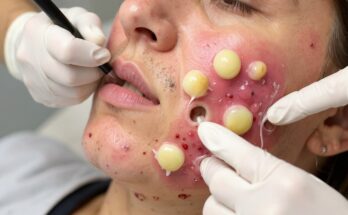
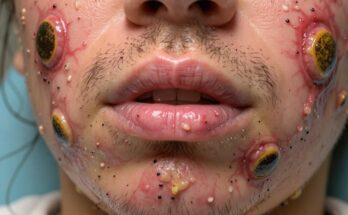
These cysts typically present as small, firm lumps beneath the skin. They can vary in size, and while often painless, they can sometimes cause discomfort depending on their size and location. Infected cysts exhibit more pronounced symptoms, such as redness, swelling, warmth to the touch, and potentially pus discharge.
Treatment Options for Sebaceous Cysts: A Range of Approaches
The appropriate treatment for a sebaceous cyst depends largely on its size, location, symptoms, and whether it’s infected.
1. The “Watch and Wait” Approach
If your cyst is small, asymptomatic (painless), and not showing signs of infection (no redness or swelling), you might not require immediate treatment. However, regular monitoring for changes in size, color, or the development of pain is crucial. Any noticeable changes warrant a visit to your doctor.
2. Home Care: Gentle Intervention
For small, uncomplicated cysts, applying warm, moist compresses for 15-20 minutes, 3-4 times daily, can sometimes encourage natural drainage. This helps reduce swelling and may expedite the cyst’s resolution.
3. The Absolute No-No: Squeezing or Popping
Resist the urge to squeeze or pop a sebaceous cyst! Unlike pimples that are superficial, these cysts are located deeper within the skin. Attempting to extract their contents increases the risk of infection, scarring, and spreading the inflammation.
4. Medical Drainage: A Temporary Solution
A physician can perform a sterile procedure to drain the cyst’s contents. This method, however, only addresses the immediate symptoms; it doesn’t remove the cyst’s sac, meaning recurrence is likely.
5. Surgical Excision: The Definitive Cure
Surgical removal is the most effective treatment, completely eliminating the cyst and its sac. Performed under local anesthesia, this minor procedure is the preferred option for painful cysts, recurring cysts, large cysts, or those located in sensitive areas. It significantly reduces the chance of recurrence and minimizes the risk of infection.
6. Antibiotics: Fighting Infection
If a sebaceous cyst becomes infected (indicated by redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and potentially pus), your doctor might prescribe oral antibiotics to combat the infection. In some cases, drainage of the infected cyst may also be necessary.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
Don’t hesitate to consult a doctor if you notice:
- Rapid growth of the cyst.
- Signs of infection (pain, redness, warmth, pus).
- The cyst is located in a sensitive or highly visible area.
- You have a history of recurring cysts.
Prevention Strategies: Proactive Skin Care
While not always preventable, certain measures can help reduce your risk:
- Minimize skin trauma: Protect your skin from unnecessary injuries that might trigger cyst formation.
- Maintain good skin hygiene: Regular cleansing helps prevent clogged pores.
- Use non-comedogenic products: Choose skincare products formulated not to clog pores.
By understanding sebaceous cysts and their various treatment options, you can make informed decisions about your skin health. Remember, early intervention and professional guidance can prevent complications and ensure effective management.