Navigating the World of Small Lumps and Cysts: A Comprehensive Guide
Dealing with a small lump or cyst can be unsettling. Understanding your options is key to making informed decisions about your health. This guide provides a detailed overview of different treatment approaches, helping you navigate this common concern.
Understanding Lumps and Cysts: A Quick Overview
Small lumps and cysts are often benign growths appearing beneath the skin’s surface. While generally harmless, their appearance can be alarming, and some may require medical attention depending on factors like size, location, pain, and potential infection. Common types include:
Common Types of Lumps and Cysts:
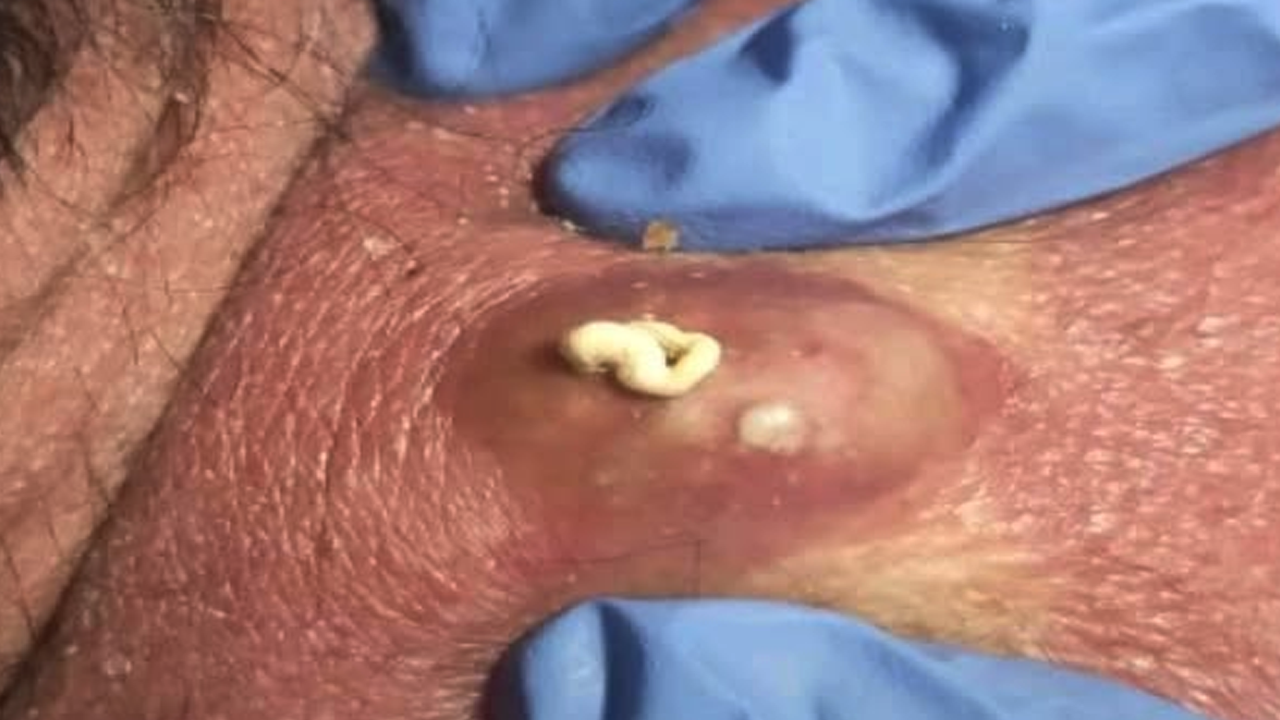
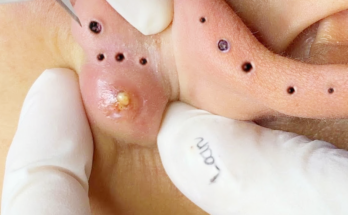
- Sebaceous (Epidermoid) Cysts: These fluid-filled sacs, often containing keratin, frequently appear on the face, neck, or torso.
- Ganglion Cysts: Typically found near joints or tendons, these cysts, filled with a jelly-like fluid, are common around wrists and hands.
- Myxoid Cysts: Located near the nail beds of fingers or toes, these fluid-filled lumps are often linked to osteoarthritis.
- Lipomas: These are benign fatty tumors that develop beneath the skin.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
While many small lumps and cysts are benign, certain signs necessitate a visit to your doctor:
- Growth: A noticeable increase in size warrants immediate attention.
- Pain or Redness: These symptoms can signal infection or inflammation.
- Fluid Leakage: Discharge from the lump requires prompt medical evaluation.
- Movement Interference: If the lump restricts movement or causes discomfort, seek professional help.
- Cosmetic Concerns: If the lump is bothersome from an aesthetic standpoint, a doctor can discuss treatment options.
- Unknown Cause: If the origin of the lump remains unclear, a biopsy might be recommended to rule out any serious conditions.
A Spectrum of Treatment Options
The approach to removing a lump or cyst depends significantly on its type, location, and the presence of any complications. Several methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
1. Watchful Waiting: A Conservative Approach
For small, asymptomatic, and non-growing lumps, your doctor might recommend monitoring the situation over time. This “wait and see” approach is suitable when the lump poses no immediate health risks. However, regular check-ups are crucial to detect any changes.
2. Needle Aspiration: A Minimally Invasive Procedure
Ideal for fluid-filled cysts (like ganglion or breast cysts), needle aspiration involves using a sterile needle to drain the fluid. While quick and minimally invasive, it’s not a permanent solution as the cyst sac remains, potentially leading to recurrence.
3. Steroid Injections: Reducing Inflammation
Corticosteroid injections directly into the cyst or surrounding tissue can effectively reduce inflammation and sometimes shrink the lump’s size. This non-surgical approach offers minimal downtime but may not completely eliminate the cyst.
4. Surgical Excision: The Definitive Solution
Surgical excision, a minor surgical procedure, offers the most definitive solution. Under local anesthesia, the entire cyst, including its capsule, is meticulously removed to minimize the risk of recurrence. While involving a small incision and potential minor scarring, it provides the most reliable long-term solution.
5. Laser Removal: Precision and Minimal Scarring
Laser removal utilizes a laser to precisely vaporize the cyst contents and remove the cyst wall. This technique is particularly well-suited for small, superficial cysts in cosmetically sensitive areas. The advantage lies in minimized scarring, although availability and cost might be limiting factors.
6. Cryotherapy: Freezing for Small Cysts
Cryotherapy employs liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy the cyst tissue. Effective for very small, superficial cysts or skin growths, it is a quick procedure, but potential skin discoloration or recurrence should be considered.
7. Antibiotics: Targeting Infection
If a lump shows signs of infection (redness, swelling, pus), antibiotics (oral or topical) are crucial to combat the infection. Note that antibiotics alone won’t remove the cyst itself; additional treatment may be needed.
Treatment Comparison Table
| Treatment Option | Invasive? | Removes Entire Cyst? | Recurrence Risk | Scarring? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | No | No | Possible | No |
| Needle Aspiration | No | No | High | No |
| Steroid Injection | No | No | Medium | No |
| Surgical Excision | Yes | Yes | Low | Yes (minor) |
| Laser Removal | Mild | Yes | Low | Minimal |
| Cryotherapy | No | Yes (small cysts) | Medium | Slight |
| Antibiotics (if infected) | No | No | N/A | No |
Further Reading and Resources
For more in-depth information, consider consulting reputable sources like the Cleveland Clinic, Healthline, and Verywell Health websites, which offer detailed articles on various types of cysts and their treatments. Remember to always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.