Understanding and Treating Blackheads: A Comprehensive Guide
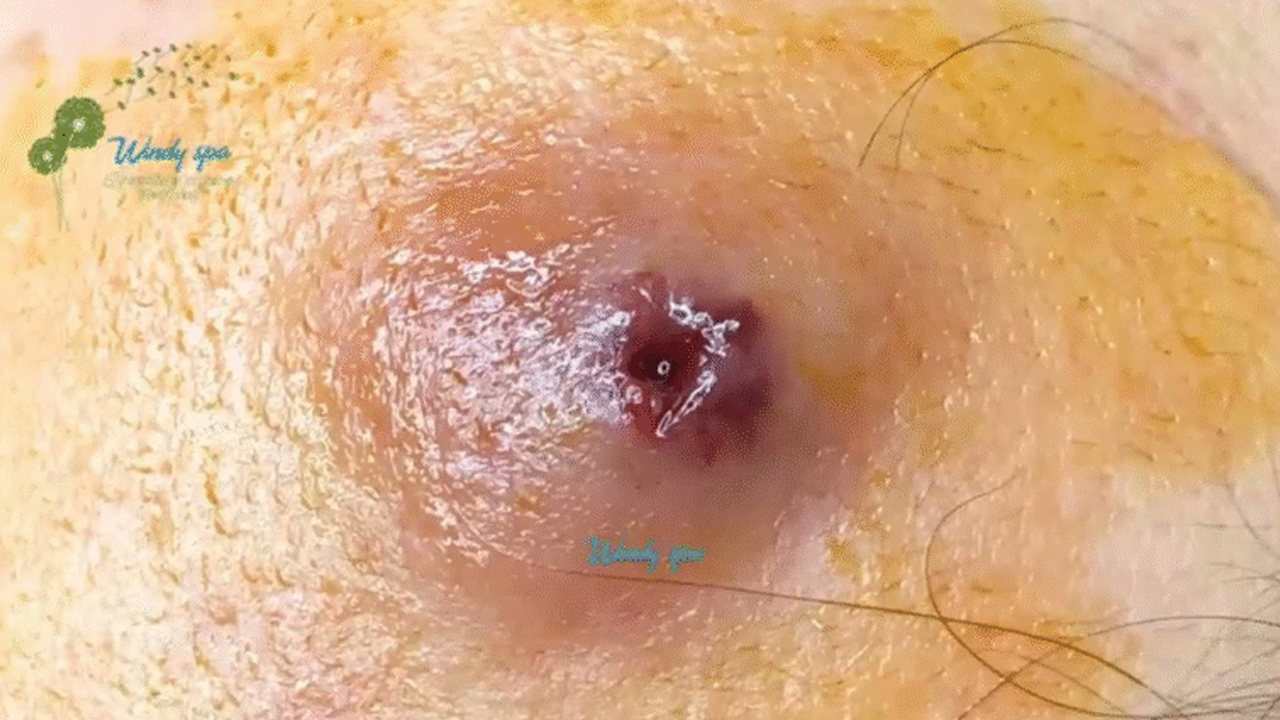
Blackheads, also known as open comedones, are a common skin concern affecting many. This unsightly blemish arises from a simple yet frustrating process: the blockage of a hair follicle. Let’s delve into the details.
The Root Cause of Blackheads
The formation of a blackhead begins with a clog within the pore. This blockage is a combination of dead skin cells, excess sebum (oil produced by the skin), and bacteria. Because the pore is sealed, this mixture cannot escape to the surface. The trapped sebum oxidizes, exposing itself to the air, which causes the characteristic dark color often associated with these blemishes. Blackheads are frequently found on the face, particularly the nose, chin, and forehead, but can also appear on the chest and other body areas.
Prevention and At-Home Care
Preventing blackheads requires a proactive approach to skincare. Regular cleansing with a gentle facial cleanser is essential for removing dirt and excess oil. Incorporating exfoliation two to three times a week helps to shed dead skin cells and prevent pore blockage. This regular maintenance helps keeps pores clear and minimizes the likelihood of blackhead formation.
Treating Existing Blackheads
While prevention is key, existing blackheads can be addressed. However, it is crucial to avoid squeezing or popping them. This practice can cause inflammation, scarring, and potentially worsen the condition by pushing the contents deeper into the skin. Instead, focus on consistent cleansing and exfoliation.
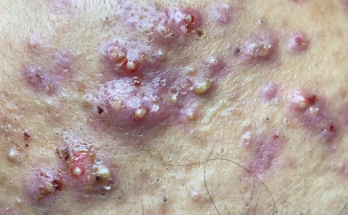
Advanced Medical Treatments for Acne and Blackheads
If blackheads persist or are part of a broader acne problem, professional help is recommended. A dermatologist can offer tailored treatment plans that may include:
Topical Treatments:
Topical treatments, such as prescription creams and gels, can effectively manage acne and blackheads by targeting the underlying bacteria or reducing excess oil production. These treatments are typically the first line of defense for mild to moderate acne.
Oral Medications:
For more severe or extensive acne, oral medications might be necessary. This often includes antibiotics to fight bacterial infections and, in some cases, stronger medications like isotretinoin for particularly stubborn acne.
Laser Therapy:
Laser therapy is a specialized option considered when other treatments have proven ineffective. It offers a targeted approach to reducing acne and blackheads.
Hormonal Acne Treatment:
For individuals experiencing hormonal acne, the focus shifts to balancing hormone levels. While it may take time, addressing the root hormonal imbalance can significantly improve skin health in the long term.
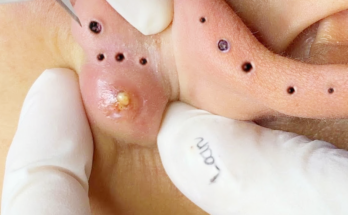
Addressing Cysts: A Different Approach
While blackheads are relatively superficial, cysts present a distinct challenge. A sebaceous or epidermoid cyst, unlike a blackhead, requires a different approach for effective removal.
The Most Effective Cyst Removal Techniques
The most effective cyst removal ensures complete removal of both the cyst contents and the entire cyst sac. This method minimizes the risk of recurrence. This procedure is often performed by a dermatologist or surgeon and typically involves these steps:
1. Diagnosis and Preparation:
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to differentiate between a cyst, lipoma, or abscess. The area is cleaned with antiseptic, and local anesthesia is administered for comfort.
2. Strategic Incision:
A small incision is made over the cyst to access the contents without rupturing the sac.
3. Content Extraction:
The keratinous material inside the cyst is gently expressed.
4. Complete Sac Removal:
The entire cyst sac is meticulously removed to prevent regrowth. This is a critical step for long-term success.
5. Wound Closure and Aftercare:
The area is cleaned, closed with sutures if needed, and covered with a sterile dressing.
The satisfaction derived from successful cyst removal is often linked to the immediate visual improvement and the knowledge that recurrence is less likely. Videos showcasing these procedures often go viral due to this instant gratification and the sense of closure they offer viewers.
Home Remedies for Non-Infected Cysts (Temporary Relief ONLY)
For non-infected cysts, some home care measures may provide temporary relief, but they are not cures:
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress can soften the cyst and potentially encourage drainage.
- Tea Tree Oil (with caution): This oil has antibacterial properties but should be used sparingly and only after a patch test. Always consult a doctor before applying essential oils to your skin.
- Maintaining Cleanliness: Gentle washing with antibacterial soap is important. Avoid picking, squeezing, or poking, as this increases the risk of infection and scarring.
Crucially: If a cyst is red, warm, painful, or oozing pus, seek immediate medical attention. These are signs of infection requiring professional treatment.
Medical Treatment Options for Cysts
Depending on the nature and severity of the cyst, a dermatologist may recommend several treatment options:
| Treatment | Use Case | Cures It? | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incision & Drainage | Infected or painful cyst | No | 2-5 days |
| Full Excision | Stubborn or recurring cyst | Yes | 1-2 weeks |
| Steroid Injection | Red, inflamed cysts | Temporary | Few days |
| Antibiotics | If infected | Only treats infection | Varies |
Choosing the right approach, whether for blackheads or cysts, depends on the specific condition and individual needs. Consulting a dermatologist is always advisable for effective diagnosis and treatment.