Conquer Those Stubborn Cysts: A Comprehensive Guide to Removal
Dealing with a persistent cyst can be frustrating. Whether it’s a sebaceous cyst, an epidermoid cyst, or another type of stubborn bump under your skin, understanding your options for removal is crucial. This detailed guide will walk you through the different approaches, helping you make an informed decision.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Cyst
The Two Key Components
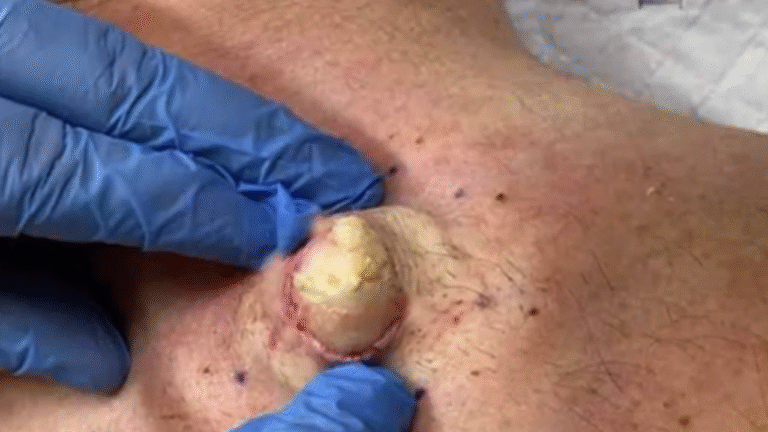
A cyst isn’t just a single entity; it’s composed of two distinct parts: the contents and the sac. The contents typically consist of a mixture of dead skin cells, keratin (a protein that makes up your skin and hair), and oil. This can sometimes appear as a pus-like or cheesy material. More importantly, the cyst sac (or cyst wall) is the outer lining, encapsulating these contents beneath your skin’s surface. This sac is the key to understanding why cysts often recur.
Why Home Remedies Fall Short
While tempting to try home remedies like squeezing or using needles, these methods are strongly discouraged. Attempting to remove a cyst at home can have several negative consequences:
- Incomplete Removal: The most likely outcome is that you will only partially remove the cyst, leaving behind portions of the sac. This practically guarantees the cyst’s return.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Breaking the skin introduces the possibility of bacteria entering the wound, leading to a painful and potentially serious infection.
- Scarring: Aggressive attempts to remove a cyst can cause permanent scarring, leaving behind an unsightly mark.
Professional Cyst Removal: Your Best Bet
Professional removal is the safest and most effective way to eliminate a cyst permanently. Several methods are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
Surgical Excision: The Gold Standard
The Procedure
Surgical excision involves making a small incision to completely remove the entire cyst, including the sac. This is the most effective method for preventing recurrence. Local anesthesia ensures the procedure is painless. The incision is then stitched closed.
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Low recurrence rate, eliminates the cyst completely.
- Cons: May leave a small scar.
Minimal Excision Technique: A Less Invasive Approach
The Procedure
This technique involves a smaller incision. The doctor will then carefully extract the cyst contents and the sac through this incision. Sutures might or might not be needed.
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Minimally invasive, resulting in smaller scars and quicker healing times.
- Cons: Higher risk of recurrence if the entire sac isn’t successfully removed. Not suitable for all cyst types or sizes.
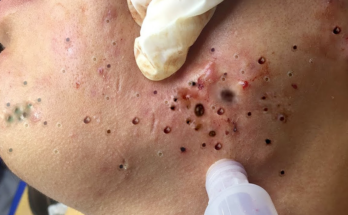
Incision and Drainage (I&D): A Temporary Fix
The Procedure
I&D is primarily used for infected or inflamed cysts. The doctor makes a small incision to drain the pus and keratin, but the cyst sac remains.
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Provides immediate relief from pain, swelling, and infection. A relatively quick procedure.
- Cons: Does not address the underlying cause, leading to a high likelihood of recurrence. Not a permanent solution.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare professional immediately if your cyst:
- Is painful, red, swollen, or draining pus.
- Keeps recurring despite home remedies.
- Is significantly affecting your movement or appearance.
- You are unsure whether it’s a cyst or a different kind of growth (lipoma, for example).
Post-Removal Care: Ensuring a Smooth Recovery
Following your doctor’s instructions carefully is essential for proper healing and preventing complications. This typically includes keeping the area clean and dry, applying antibiotic ointment as directed, and monitoring for signs of infection (redness, increased heat, pus).
Types of Cysts: A Closer Look at Sebaceous Cysts
Sebaceous cysts (also known as epidermoid cysts) are benign, slow-growing lumps often found on the face, neck, or trunk. They’re usually painless unless infected or inflamed. While generally harmless, their size, infection, or recurrence can make them a significant concern.
Summary Table: Cyst Removal Methods at a Glance
| Treatment Method | Removes Cyst Sac? | Recurrence Risk | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incision & Drainage | No | High | Infected, painful cysts |
| Surgical Excision | Yes | Low | Large, recurrent cysts |
| Minimal Excision | Yes | Moderate | Small, superficial cysts |
Remember, consulting a dermatologist or other healthcare professional is the best way to determine the appropriate treatment for your specific cyst. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice to ensure a safe and effective removal.