Understanding and Treating Blackhead Cysts: A Comprehensive Guide
This blog post delves into the often-confusing world of blackhead cysts, explaining their nature, treatment options, and how to prevent their recurrence. We’ll explore the differences between simple blackheads and their more complex, cystic counterparts.
What Exactly is a Blackhead Cyst?
The Difference Between a Blackhead and a Blackhead Cyst
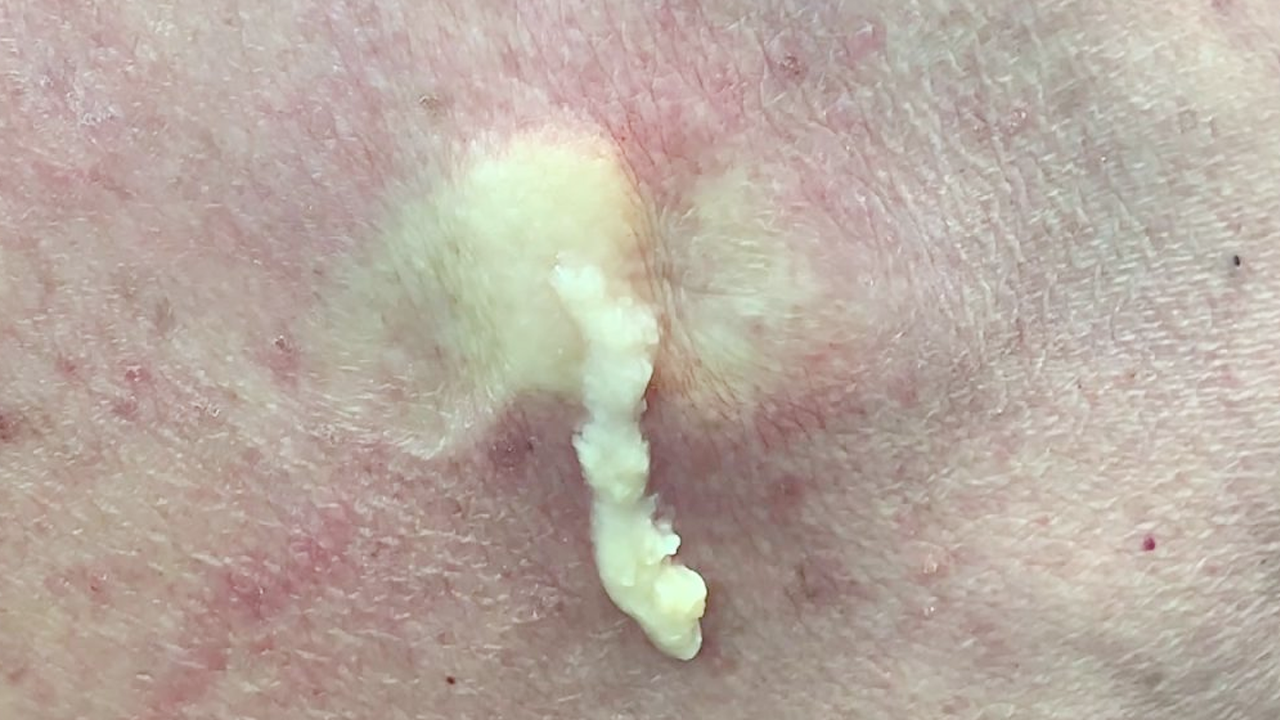
Unlike a typical blackhead, which is a clogged pore filled primarily with oil and dead skin cells, a blackhead cyst – also known as an epidermoid cyst or sebaceous cyst – is a deeper, more significant issue. These dome-shaped lumps often appear beneath the skin’s surface, sometimes with a visible dark spot (the clogged pore). Crucially, these cysts contain keratin, a protein found in skin and hair, not just oil. Sebaceous cysts originate from oil glands, whereas epidermoid cysts stem from hair follicle cells. This distinction impacts treatment approaches.
Home Care: Temporary Relief, Not a Cure
While home remedies offer temporary comfort, they cannot fully eliminate a blackhead cyst. Attempting to squeeze or pop it at home is strongly discouraged, as this can lead to infection, scarring, and the deeper embedding of the cyst’s contents.
Gentle Approaches for Minor Discomfort
Applying a warm compress for 15-20 minutes, two to three times daily, can help soften the skin and potentially encourage drainage if the cyst is inflamed. This provides temporary relief from swelling and tenderness, but it won’t remove the cyst itself.
Over-the-Counter Topical Treatments: Limited Effectiveness
Over-the-counter products like benzoyl peroxide (for minor infections), salicylic acid (to reduce pore clogging), and retinoids (like adapalene, to decrease keratin buildup) may offer some benefit in preventing new cysts or managing minor inflammation around an existing one. However, these treatments won’t remove the cyst itself.
Medical and Surgical Interventions: Achieving Permanent Removal
For definitive and safe removal of a blackhead cyst, professional medical intervention is essential. A dermatologist can accurately assess the situation and recommend the most appropriate treatment, choosing from several options:
Incision and Drainage (I&D): A Quick Fix, But with Caveats
If the cyst is infected or significantly inflamed, incision and drainage may be performed. This involves a small incision to drain the pus and keratin. While providing immediate relief, I&D leaves the cyst sac intact, increasing the likelihood of recurrence.
Surgical Excision: The Gold Standard for Permanent Removal
Surgical excision is the most effective method for long-term removal. This procedure involves completely removing the entire cyst sac, minimizing the risk of recurrence. Two techniques exist: standard excision, resulting in a small scar, and minimal excision, which aims for less scarring but might have a slightly higher recurrence risk.
Corticosteroid Injections: Reducing Inflammation
For inflamed but uninfected cysts, a corticosteroid injection can rapidly reduce swelling and discomfort. This approach doesn’t remove the cyst sac, but it can significantly shrink the cyst temporarily.
Post-Treatment Care and Prevention
Regardless of the treatment method, proper aftercare is crucial to minimize the risk of infection and promote healing. This involves keeping the area clean and dry, applying any prescribed ointments (e.g., antibiotic creams), and avoiding touching or squeezing the treated area. Signs of infection (increased pain, redness, warmth, or pus) warrant immediate medical attention.
Preventing future blackhead cysts involves maintaining a consistent skincare routine, including gentle cleansing with non-comedogenic products and the regular use of retinoid creams to regulate skin cell turnover. Avoiding picking or squeezing existing blemishes is paramount to prevent recurrence. For individuals prone to recurring cysts, a dermatologist can discuss long-term topical or oral treatment options.
Summary Table: Comparing Treatment Options
| Treatment | Removes Cyst Sac? | Recurrence Risk | Scarring? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warm Compress | No | High | None |
| Incision & Drainage | No | Moderate-High | Minimal |
| Steroid Injection | No | High | None |
| Surgical Excision | Yes | Very Low | Small Scar |
| Minimal Excision | Yes | Low-Moderate | Very Small Scar |
Remember, seeking professional guidance from a dermatologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and the most effective treatment plan for both blackheads and blackhead cysts. Don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment if you’re experiencing persistent or problematic cysts.