Decoding the Mystery: A Comprehensive Guide to Cyst Removal
This blog post delves into the fascinating world of cyst removal, offering a detailed, step-by-step explanation of the procedure and providing valuable insights into causes, prevention, and treatment options. Forget the shock value often associated with online videos; we’re focusing on the medical facts and empowering you with knowledge.
Understanding Cysts: Types and Causes
What Exactly is a Cyst?
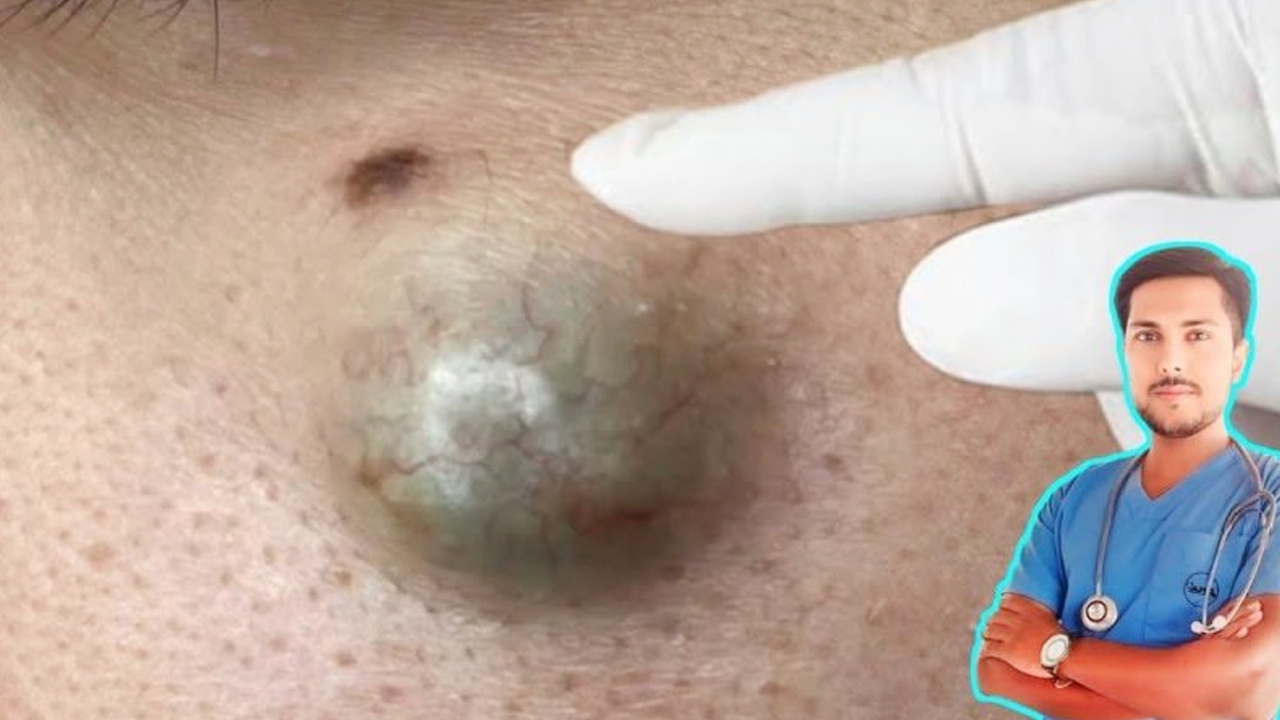
A cyst is essentially a sac-like structure within body tissue, filled with fluid, pus, or other substances. These aren’t always problematic, but their presence can cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns, depending on location and size. Several types exist, each with its own unique characteristics and causes.
Common Types of Cysts
- Epidermoid (Sebaceous) Cysts: These frequently appear on the face, neck, and torso, arising from trapped skin cells or keratin beneath the skin’s surface. Blocked hair follicles or skin trauma often play a role in their development.
- Pilonidal Cysts: Located near the tailbone, these cysts usually result from ingrown hairs or prolonged pressure on the area. Individuals who sit for extended periods or have excessive body hair are at a higher risk.
- Ovarian Cysts: These cysts form within the ovaries and are more common in women. Hormonal imbalances, pregnancy, or conditions like endometriosis can contribute to their formation. Symptoms may include pelvic pain, bloating, or irregular periods.
- Other Cysts: Numerous other cyst types exist, located in various parts of the body. A proper diagnosis is crucial for appropriate treatment.
Unraveling the Mystery: What Causes Cysts?
The exact cause of cyst formation can vary depending on the type of cyst. However, common contributing factors include:
- Blocked glands or ducts: This is especially relevant in sebaceous cysts, where blocked oil glands prevent the natural drainage of sebum.
- Infections or inflammations: Infections can lead to the formation of pus-filled cysts.
- Ingrown hairs: This is a frequent cause of pilonidal cysts.
- Trauma or irritation: Skin injuries can sometimes trigger cyst development.
- Genetic predisposition: In some cases, a family history of cysts may increase the risk.
Diagnosis and Medical Intervention: A Step-by-Step Approach
Diagnosing the Problem: What to Expect
Accurate diagnosis is the first step in managing a cyst. Your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination to assess the cyst’s size, location, and any associated symptoms. Further investigations, such as ultrasound or MRI scans, might be necessary to visualize deeper or internal cysts. In rare cases, a biopsy may be performed to rule out cancerous growths.
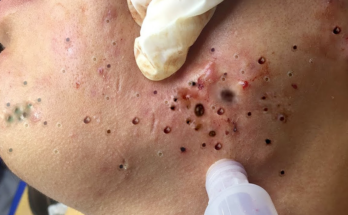
The Surgical Removal Process: A Detailed Overview
Surgical removal is often the most effective treatment for symptomatic cysts, especially larger ones or those prone to recurrence. This procedure, performed by a qualified medical professional in a sterile environment, typically involves these steps:
- Preparation: The area is thoroughly cleaned and a local anesthetic is administered to numb the site, ensuring patient comfort.
- Incision: A small, precise incision is made directly over the cyst using a scalpel.
- Cyst Removal: The entire cyst sac (capsule) is carefully and completely removed. This critical step minimizes the risk of recurrence, which is a common issue if only the contents are drained.
- Closure: The incision is closed using sutures (stitches), which may be dissolvable or require later removal. A sterile dressing is applied to protect the wound.
Post-Operative Care: Ensuring Proper Healing
Post-operative care is crucial for optimal healing and minimizing complications. This usually includes:
- Maintaining cleanliness of the area.
- Applying any prescribed ointments or creams.
- Monitoring for signs of infection (redness, swelling, increased pain).
- Attending follow-up appointments for stitch removal (if applicable) and wound assessment.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
While surgical excision is often the preferred method, some smaller, uncomplicated cysts might respond to less invasive treatments. These include:
- Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses can sometimes help drain small, non-infected cysts.
- Steroid injections: These injections can reduce inflammation and potentially shrink the cyst’s size.
- Antibiotics: If a cyst becomes infected, antibiotics are necessary to combat the infection.
- Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts may not require any intervention and can be monitored for changes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cysts are benign, it’s essential to seek medical advice if you notice any of the following:
- Pain, redness, or warmth around the cyst (signs of infection).
- Rapid growth or changes in the cyst’s appearance.
- Fever or other systemic symptoms.
- Restricted movement or discomfort due to the cyst’s location.
This detailed explanation should provide a clearer understanding of cysts and their treatment. Remember, always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations. Never attempt self-treatment of cysts.