Understanding and Tackling Blackheads and Cystic Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
This blog post dives deep into the world of blackheads and cystic acne, exploring their causes, effective treatments, and preventative measures. We’ll cover both professional and at-home solutions to help you achieve clearer, healthier skin.
The Science Behind Blackheads and Cystic Acne
Blackheads: Unclogged Pores and Oxidized Sebum
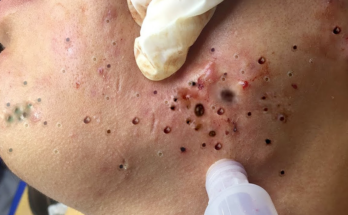
Blackheads, also known as open comedones, arise from a simple yet frustrating process: clogged pores. Dead skin cells, sebum (the skin’s natural oil), and bacteria become trapped within the hair follicle. This blockage prevents the debris from escaping, leading to the characteristic dark appearance. The dark color isn’t dirt, but rather melanin in the sebum that oxidizes upon exposure to air. These blemishes commonly appear on the face (nose, chin, forehead), chest, and back.
Cystic Acne: Deep-Seated Inflammation
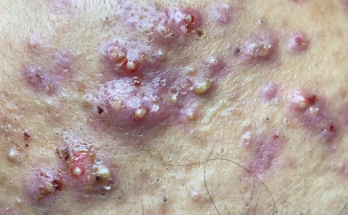
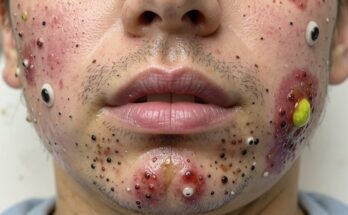
Cystic acne, on the other hand, is a more severe form of acne. It involves inflamed, painful cysts that form deep within the skin. This type of acne is often a complex interplay of hormonal imbalances, excessive sebum production, and bacterial activity. The result is painful, pus-filled lumps that can significantly impact your confidence and well-being.
Preventing Blackheads: Proactive Skincare
Prevention is key when it comes to blackheads. A consistent skincare routine is your first line of defense:
- Gentle Cleansing: Wash your face twice daily with a mild, sulfate-free cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can irritate the skin.
- Regular Exfoliation: Exfoliate two to three times a week to remove dead skin cells and prevent pore clogging. Chemical exfoliants, such as salicylic acid, are often more effective than physical scrubs for blackheads.
- Clay Masks: Incorporate a clay mask once or twice a week to absorb excess oil and draw out impurities from your pores. Kaolin or bentonite clay are excellent choices.
- Non-comedogenic Products: Always opt for skincare and makeup products labeled “non-comedogenic,” meaning they are formulated to minimize pore clogging.
Treating Blackheads: Targeted Approaches
While prevention is crucial, existing blackheads can be addressed with these methods:
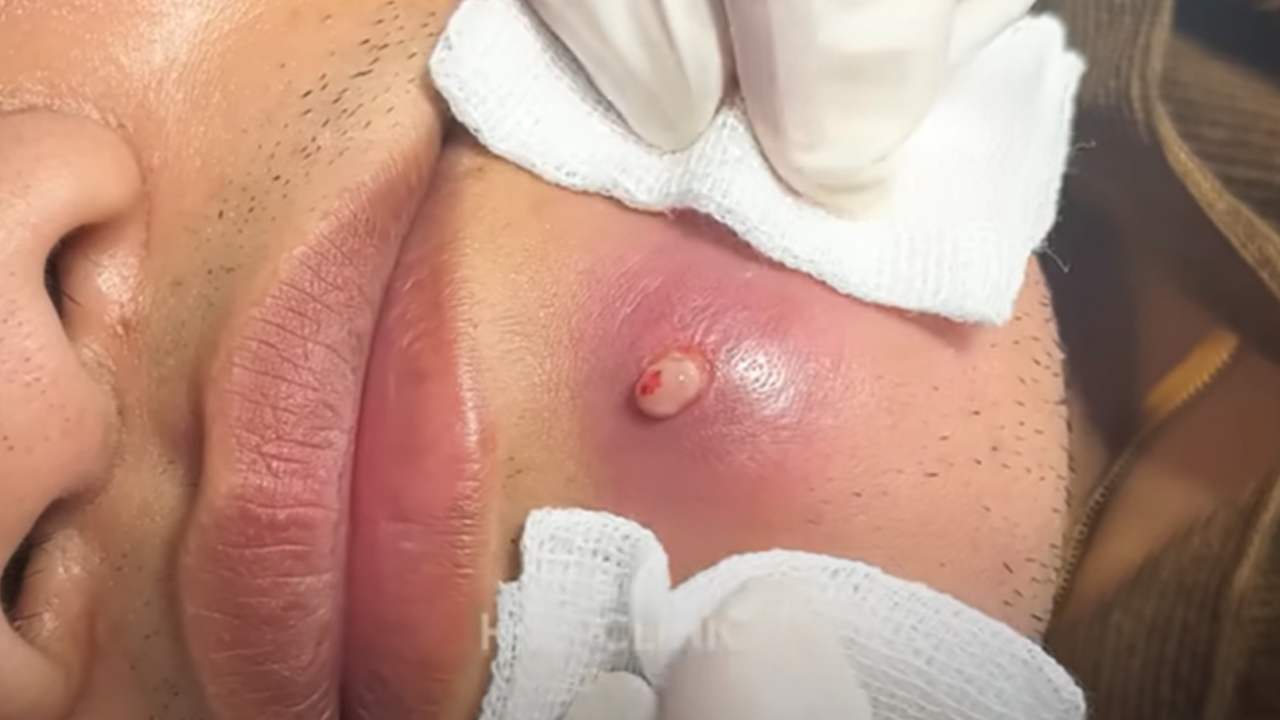
- Comedone Extractors: These specialized tools can gently remove blackheads, but use them carefully to avoid skin damage. Always sterilize the tool before and after each use. Steaming your face beforehand can help soften the blackheads.
- Salicylic Acid Treatments: Salicylic acid’s ability to penetrate pores and dissolve oil makes it highly effective against blackheads. Look for cleansers, toners, or serums containing this ingredient.
- Professional Extraction: A dermatologist or esthetician can safely and effectively extract blackheads using specialized techniques and tools.
Combating Cystic Acne: A Multi-pronged Strategy
Cystic acne often requires a more comprehensive approach, frequently involving a combination of professional and at-home treatments:
Topical Treatments: Targeting Inflammation and Bacteria
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This antibacterial agent helps to reduce the bacteria (specifically Propionibacterium acnes) that contribute to acne. It also dries excess sebum. Use a 2.5% to 5% concentration.
- Salicylic Acid: Its exfoliating properties unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
- Topical Retinoids (e.g., tretinoin, adapalene): These vitamin A derivatives increase skin cell turnover, reduce inflammation, and unclog pores. Start with a low concentration and apply at night.
Oral Medications: For Moderate to Severe Cases
If topical treatments prove insufficient, your dermatologist may prescribe oral medications:
- Oral Antibiotics: These help control bacterial growth and reduce inflammation. Examples include tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): This powerful medication is reserved for severe, unresponsive cases. While highly effective, it has significant potential side effects, requiring careful monitoring by a dermatologist.
Other Cystic Acne Treatments
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress can ease pain and swelling by promoting drainage.
- Hormonal Therapy: For women, hormonal imbalances can play a significant role. Your dermatologist may recommend birth control pills to regulate hormones.
Professional Expertise: When to Seek Help
For persistent or severe acne, especially cystic acne, consulting a dermatologist is vital. They can accurately diagnose your condition, determine the underlying causes, and create a personalized treatment plan. This may involve a combination of topical and oral medications, professional extractions, or advanced procedures like laser therapy. They can also help address any underlying hormonal issues contributing to your acne. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help—it can make a significant difference in achieving clear, healthy skin. Ignoring severe acne could lead to permanent scarring.
Lifestyle Factors and Overall Skin Health
While treatments are essential, a holistic approach considers lifestyle factors:
- Diet: While not definitively proven, some studies suggest that dairy and high-glycemic foods may worsen acne.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, potentially increasing sebum production. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or exercise into your routine.
- Sun Protection: Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your skin from sun damage, especially when using acne treatments that increase sun sensitivity.
Remember, consistent effort and a tailored approach are key to managing and ultimately overcoming blackheads and cystic acne.