Conquering Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Treating Cystic Acne and Blackheads
This guide delves into the effective management of cystic acne and blackheads, two common yet distinct acne forms. We’ll explore their differences, effective treatment strategies, and preventative measures to keep your skin clear and healthy.
Understanding the Differences: Cystic Acne vs. Blackheads
Before diving into treatments, it’s crucial to understand the differences between these two acne types. This knowledge will guide you towards the most appropriate course of action.
Cystic Acne: The Inflammatory Beast
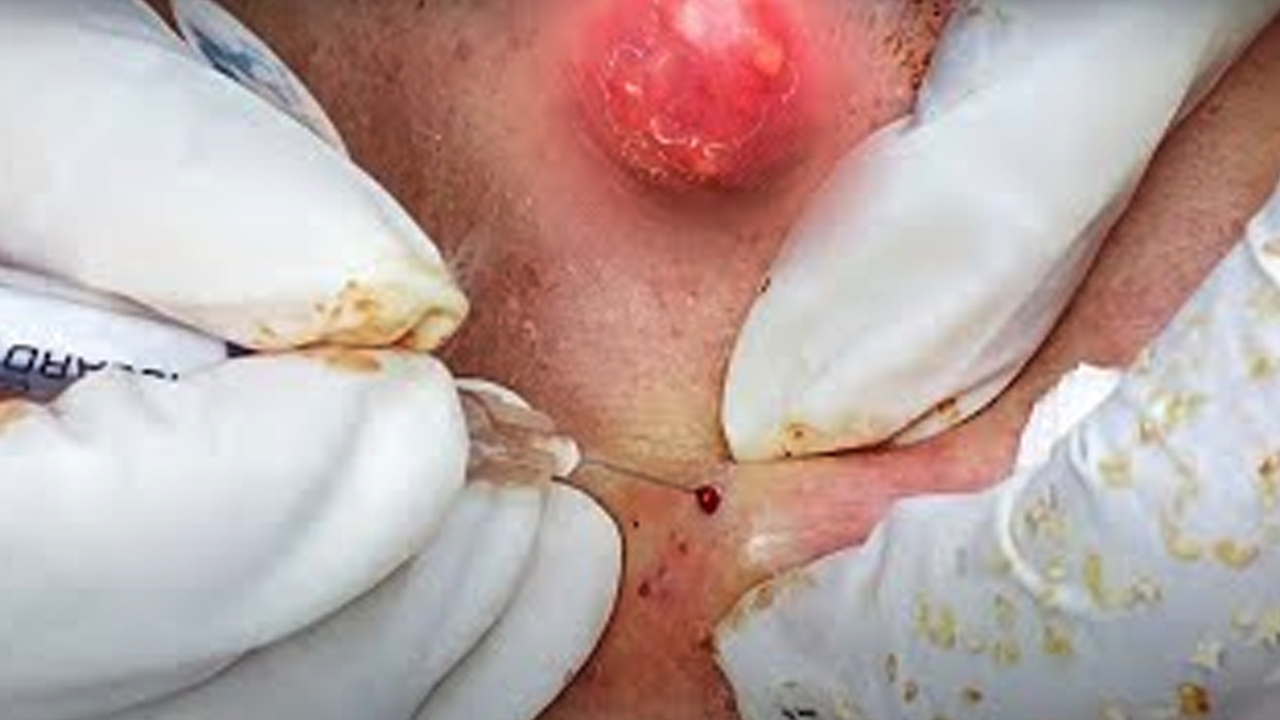
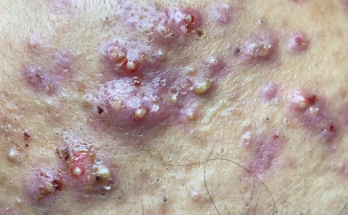
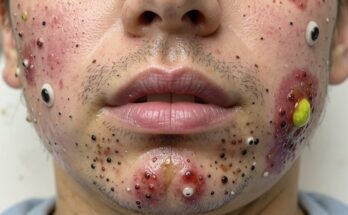
Cystic acne presents as large, painful, red lumps buried deep within the skin. These cysts are filled with pus and, if mishandled, can lead to persistent scarring. Their deep-seated nature makes them significantly more challenging to treat than blackheads. The inflammation associated with cystic acne is a key characteristic.
Blackheads: The Stubborn Clogged Pores
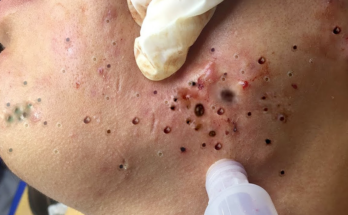
Blackheads, on the other hand, are open comedones—clogged pores filled with a mixture of oil and dead skin cells. The dark color arises from oxidation upon exposure to air. While usually not painful, blackheads can be persistent and unsightly.
Tackling Cystic Acne: A Multi-pronged Approach
Cystic acne often necessitates a combination of at-home care and professional medical intervention. Never attempt to squeeze or pick at these cysts; doing so can exacerbate inflammation and significantly increase scarring.
At-Home Care for Cystic Acne
Gentle care is key. Apply warm compresses for 10-15 minutes, twice daily, to soothe inflammation and encourage drainage. Over-the-counter products containing benzoyl peroxide (to combat bacteria) and salicylic acid (to unclog pores) can be helpful adjuncts. Ice packs can provide temporary pain relief.
Medical Interventions for Cystic Acne
For significant or persistent cystic acne, professional help is crucial. A dermatologist can prescribe a range of treatments, including:
- Topical retinoids: These regulate skin cell turnover, preventing pore blockage. Examples include adapalene (Differin) and tretinoin.
- Oral antibiotics: Medications like doxycycline and minocycline help reduce bacterial inflammation. These are usually prescribed for short durations to minimize antibiotic resistance.
- Hormonal treatments: Birth control pills or spironolactone can regulate hormone levels, particularly beneficial for women with hormonal acne.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): Reserved for severe, treatment-resistant cases, this medication significantly reduces sebum production. It requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
- Corticosteroid injections: These provide rapid relief from individual, inflamed cysts by directly reducing inflammation.
Managing Blackheads: Effective Home and Professional Treatments
Blackheads are often manageable with home remedies, but professional intervention may sometimes be necessary for stubborn cases.
At-Home Blackhead Management
Gentle exfoliation is key. Use salicylic acid cleansers to unclog pores, and consider incorporating retinoids (adapalene, tretinoin) to prevent future blockages. Clay or charcoal masks can effectively absorb excess oil and impurities. Resist the urge to squeeze blackheads—this causes trauma and potential scarring.
Professional Blackhead Treatments
A dermatologist can perform various procedures for more stubborn blackheads:
- Comedone extraction: A safe and effective method for removing blackheads using sterile tools.
- Chemical peels: These exfoliate the skin using acids like glycolic or salicylic acid.
- Microdermabrasion or laser treatments: These offer more aggressive exfoliation and oil-reduction options.
Preventing Future Breakouts: A Proactive Approach
Preventing acne requires a consistent approach to skincare and lifestyle.
Key Preventative Measures
- Cleanse twice daily: Use a gentle cleanser suited to your skin type.
- Use non-comedogenic products: Choose skincare and makeup that won’t clog pores.
- Avoid heavy oils and greasy products: These contribute to pore blockages.
- Change pillowcases regularly: Clean bedding prevents the transfer of bacteria and oils.
- Remove makeup before bed: Sleeping with makeup on clogs pores and encourages breakouts.
Recommended Products
While specific product recommendations depend on individual needs, incorporating products containing salicylic acid (for exfoliation), benzoyl peroxide (for antibacterial action), and a non-comedogenic moisturizer are often beneficial. Always select an oil-free sunscreen for daily sun protection. Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice on product selection.