Understanding and Treating Epidermal Cysts: A Comprehensive Guide
Epidermal cysts, sometimes called sebaceous cysts, are benign, fluid-filled sacs that develop beneath the skin’s surface. These lumps, commonly found on the face, scalp, back, and chest, are typically painless. However, their size and location can sometimes cause discomfort or even pose health risks if left untreated. This guide explores epidermal cysts, focusing specifically on the successful surgical removal of a large mid-chest cyst, covering the procedure, recovery, and crucial post-operative care.
What are Epidermal Cysts?
Formation and Characteristics
Epidermal cysts form when hair follicles or skin pores become blocked, trapping oil, dead skin cells, and other debris. This buildup creates a closed sac beneath the skin’s surface. The size of these cysts can vary greatly. While small cysts may be unnoticeable, larger ones can put pressure on surrounding tissue, causing discomfort, irritation, and potentially leading to infection or inflammation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Minor cysts often require no treatment, but larger cysts, those causing significant discomfort, or those showing signs of infection warrant medical intervention. A large cyst on the mid-chest, for instance, can interfere with movement, chafe against clothing, and increase the risk of infection due to its location.
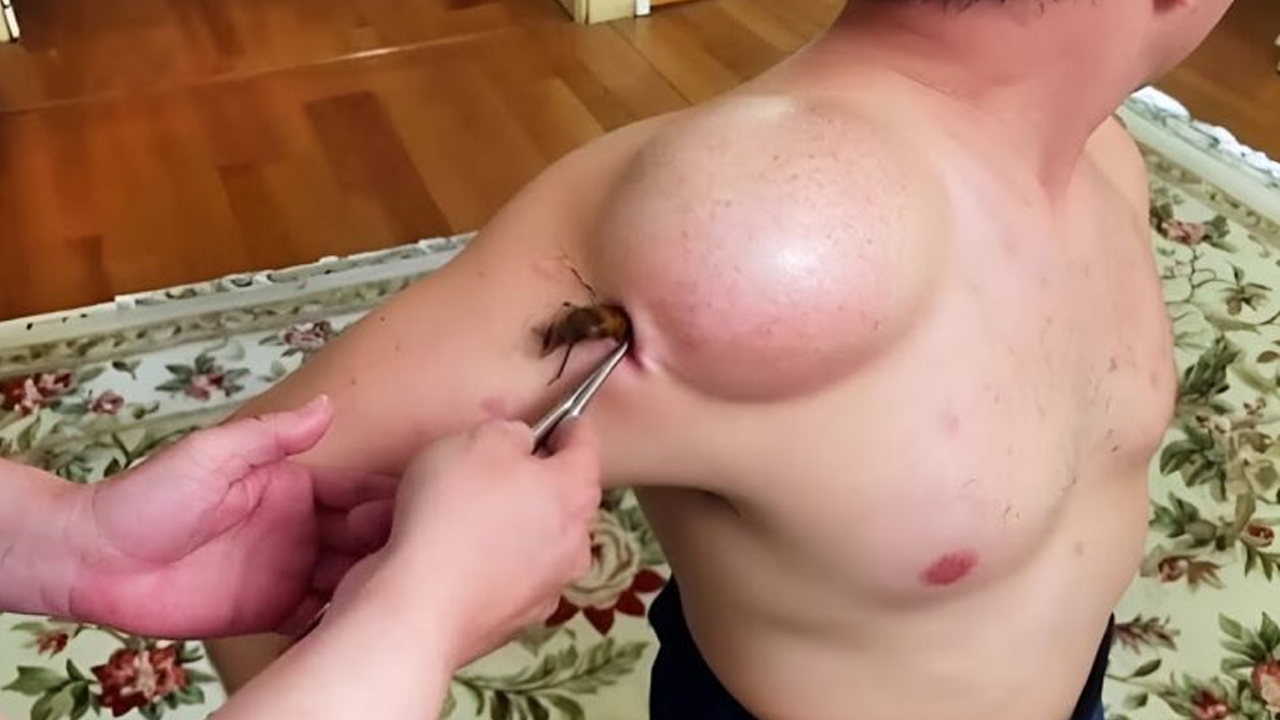
Surgical Removal of a Large Mid-Chest Epidermal Cyst: A Case Study
This section details the process of surgically removing a sizable epidermal cyst located on the mid-chest. This approach is often the best option for larger cysts to prevent recurrence and associated complications.
1. Pre-Operative Assessment and Planning
The journey begins with a thorough consultation with a dermatologist or surgeon. This involves a comprehensive examination of the cyst, assessing its size, location, and any potential risks. A complete medical history, including allergies and previous skin conditions, is reviewed to ensure patient safety and optimize the surgical plan. In this case, the decision was made to surgically remove the cyst entirely, the preferred method for larger cysts to minimize the chances of regrowth. Drainage alone often leaves behind cyst remnants, increasing the risk of recurrence.
2. The Surgical Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Anesthesia and Preparation
The procedure begins with preparing the area in a sterile environment. Local anesthesia is typically used to numb the area around the cyst, ensuring patient comfort during the procedure. For larger or more complexly located cysts, general anesthesia might be considered to ensure complete relaxation and optimal surgical conditions.
Incision and Cyst Excision
A small incision is carefully made over the cyst. The surgeon delicately dissects the surrounding tissue to isolate the cyst from the underlying skin and structures. Complete removal of the entire cyst capsule is crucial to prevent regrowth. This meticulous step requires precision, especially with larger cysts, to avoid damaging nearby nerves, blood vessels, or muscles.
Wound Closure and Dressing
Once the cyst is completely removed, the incision site is carefully closed using sutures (stitches). These may be dissolvable or require removal after approximately a week. A sterile dressing is then applied to protect the wound.
3. Post-Operative Care and Recovery
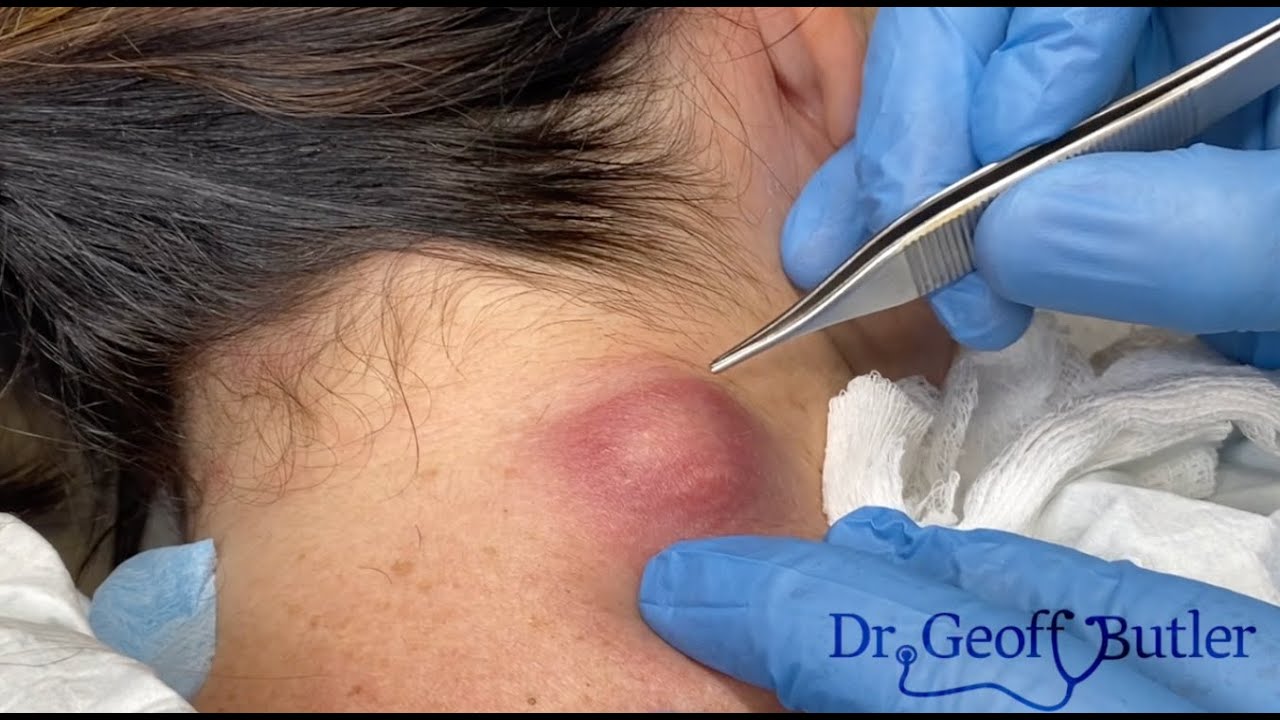
Recovery after this procedure varies depending on factors such as the cyst’s size, surgical complexity, and the patient’s overall health.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Following the surgery, a bandage is applied to protect the incision. Maintaining cleanliness and dryness is paramount to prevent infection. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activity or heavy lifting for the initial days to facilitate proper healing.
Pain Management and Potential Complications
Mild discomfort or tenderness is common in the first few days. Over-the-counter pain relievers often suffice, but stronger medication may be prescribed if necessary. Swelling and bruising are expected and usually subside within a few days. While rare, infection is a possible complication. Patients are instructed to watch for signs such as increased redness, warmth, or discharge from the incision site and contact their healthcare provider immediately if any arise.
Follow-up Appointments and Long-Term Care
Follow-up appointments allow the surgeon to monitor healing progress, check for complications, and remove non-dissolvable stitches. Once healed, minimizing sun exposure to the area helps minimize scarring. Moisturizing the skin around the incision can aid the healing process.
The Advantages of Complete Cyst Removal
Complete surgical removal offers significant advantages. Most importantly, it eliminates the risk of recurrence. Furthermore, it prevents potential infection and long-term irritation associated with the cyst. While scarring is a possibility with any surgical procedure, the scar from a well-executed cyst removal is usually minimal and fades over time with proper aftercare. Most patients can return to their normal routines once the wound has healed.
Conclusion
Surgical removal of a large mid-chest epidermal cyst is a relatively straightforward procedure that provides considerable relief from discomfort and aesthetic concerns. Choosing surgical intervention helps avoid complications, ensures complete cyst removal, and minimizes recurrence. If you’re experiencing discomfort from an epidermal cyst, consult a dermatologist or surgeon to discuss your treatment options. Effective management and professional removal can quickly alleviate symptoms and restore comfort.