The Giant Gluteal Abscess: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing This Painful Condition
A giant gluteal abscess is a significant infection, characterized by a large, pus-filled swelling in the buttock area. This painful condition stems from bacterial infection, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus, and demands immediate medical attention to prevent serious complications. Ignoring this condition can lead to considerable discomfort and potentially life-threatening consequences. Let’s explore this condition in detail.
Understanding the Nature of a Giant Gluteal Abscess
What is a Gluteal Abscess?
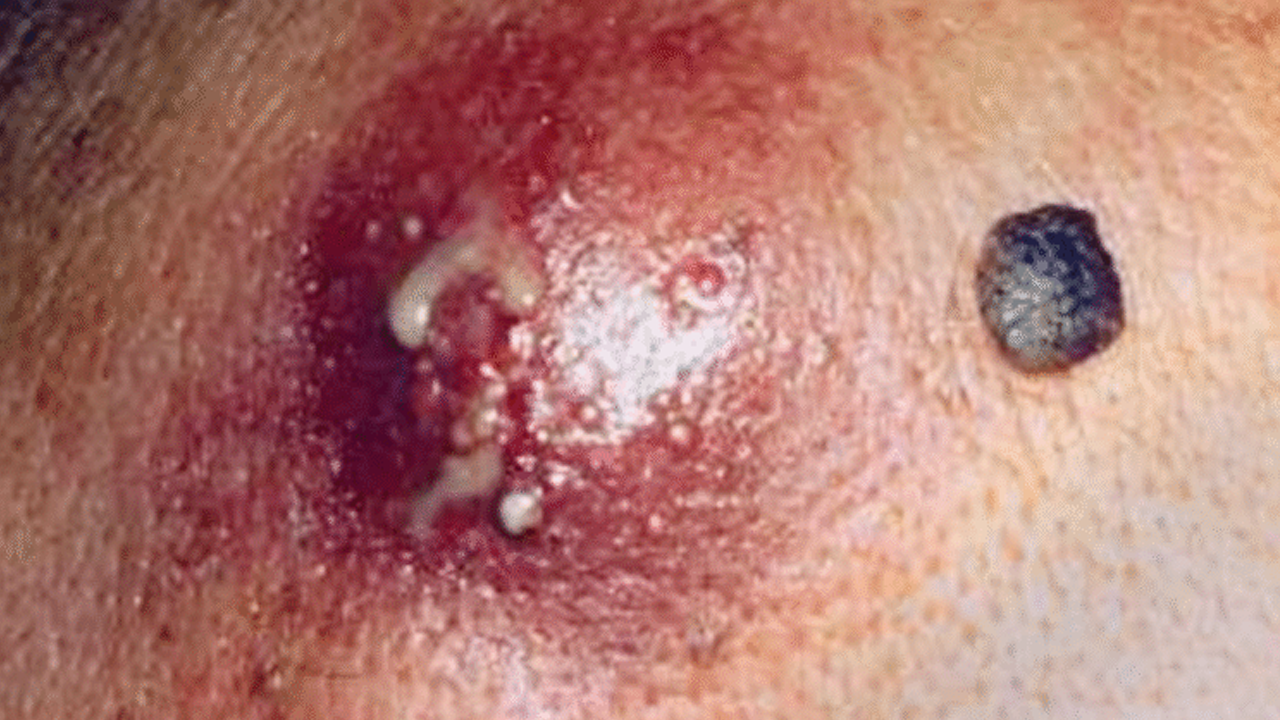
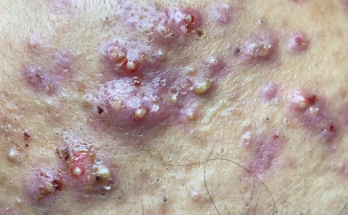
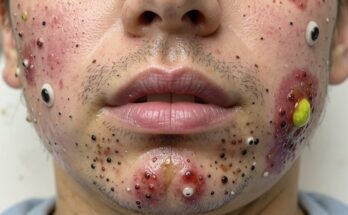
A gluteal abscess is a localized infection beneath the skin of the buttock. When the abscess reaches a considerable size, it’s classified as “giant,” signifying its severity and the urgent need for medical intervention. The pus buildup causes intense pain and swelling, making even simple movements excruciating.
The Root Cause of Infection
The primary culprit behind gluteal abscess formation is bacterial infection, most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Other bacteria may also be involved, contributing to the infection’s complexity. This bacterial invasion creates a pocket of pus that continues to grow, necessitating prompt medical care.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Giant Gluteal Abscesses
Ignoring a giant gluteal abscess is not an option. Effective treatment requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on drainage and combating the infection.
Immediate Medical Intervention: The First Step
Home remedies are insufficient for a giant gluteal abscess. Immediate medical attention is crucial. Delaying treatment can lead to the spread of infection throughout the body (sepsis), tissue damage (necrosis), and other severe complications. Seeking professional medical help is paramount.
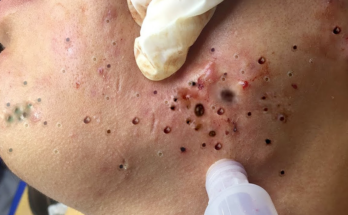
Surgical Drainage: The Cornerstone of Treatment
The primary treatment is incision and drainage (I&D). This minor surgical procedure involves making a small incision to drain the pus. This is often performed under local anesthesia, sometimes requiring a drainage catheter to ensure complete removal of the infectious material. In some cases, particularly for deep or complex abscesses, percutaneous drainage guided by ultrasound or CT scans may be employed. This less-invasive technique uses a needle to drain the abscess, followed by catheter placement.
Antibiotic Therapy: Eradicating the Infection
Following drainage, antibiotics are prescribed to fight the infection. The choice of antibiotic depends on the specific bacteria identified (often through a pus culture). Common options include amoxicillin/clavulanate, cephalexin, and metronidazole. The duration of antibiotic therapy typically spans 7 to 14 days. Importantly, antibiotics alone are insufficient for a giant abscess; drainage is essential.
Post-Treatment Care and Wound Management
After the procedure, careful wound care is vital. Daily cleaning with sterile saline and regular dressing changes are necessary. Avoiding pressure on the wound and monitoring for signs of infection (fever, increased pain, redness) are crucial for proper healing, which can take 1-3 weeks.
Preventing Future Abscesses: Proactive Measures
While treatment focuses on the immediate problem, preventing future abscesses is equally important.
Hygiene and Skin Care
Maintaining good hygiene, including regular washing and drying of the buttock area, is essential. Avoiding skin trauma, such as friction from prolonged sitting or wearing damp clothing, helps reduce the risk of infection. Early treatment of skin conditions like acne or folliculitis prevents them from escalating into abscesses.
Managing Underlying Conditions
Individuals with diabetes, HIV, or weakened immune systems are at higher risk for abscess formation. Managing these underlying health conditions effectively lowers the likelihood of recurring abscesses. Chronic abscesses may warrant investigation for conditions such as hidradenitis suppurativa or Crohn’s disease.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Don’t hesitate to seek urgent medical care if you experience:
- High fever or chills
- Spreading redness around the abscess
- Severe pain making sitting or walking impossible
- Signs of a systemic infection (e.g., rapid heart rate, low blood pressure)
A giant gluteal abscess is a serious condition requiring prompt and comprehensive medical management. Early intervention significantly improves the chances of a full recovery and prevents serious, potentially life-threatening complications.